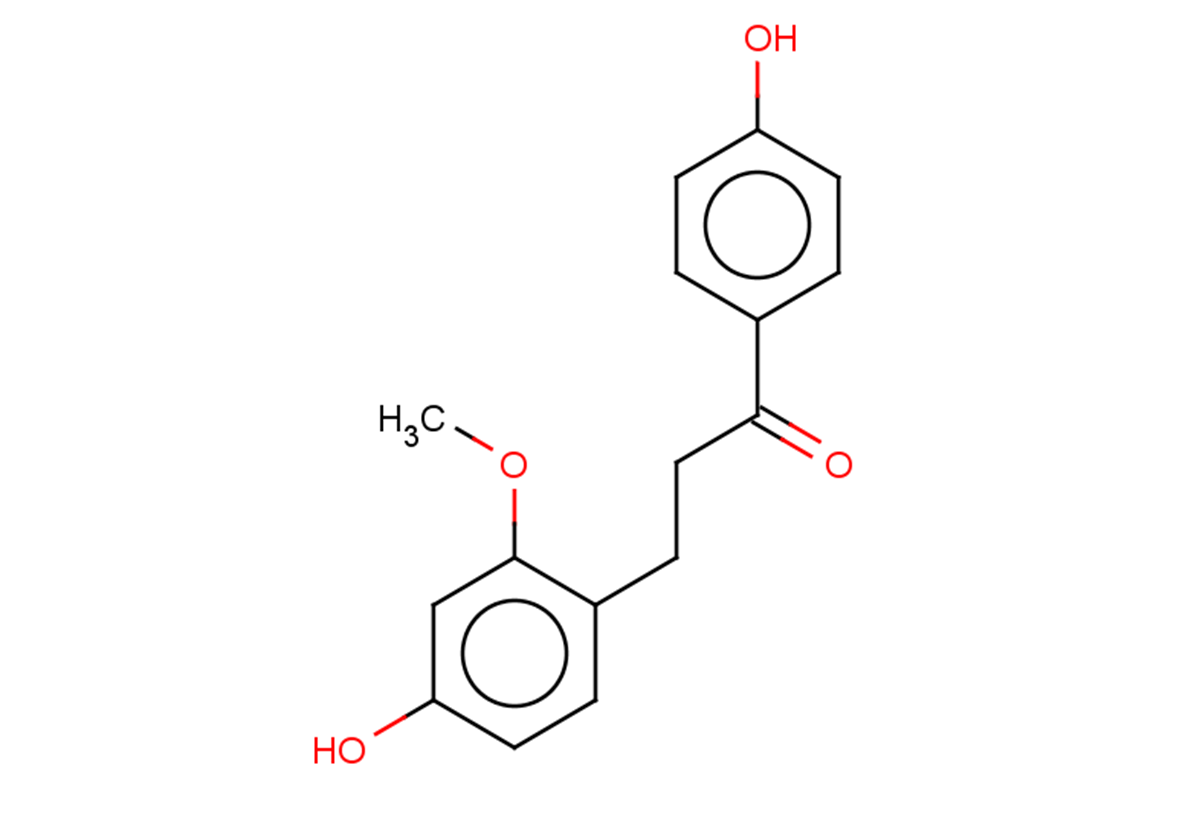
Loureirin C
CAS No. 116384-24-8
Loureirin C( —— )
Catalog No. M23338 CAS No. 116384-24-8
Loureirin C can inhibit the activities of thrombin in vitro effectively.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 222 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 331 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 536 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 777 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1044 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameLoureirin C
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionLoureirin C can inhibit the activities of thrombin in vitro effectively.
-
DescriptionLoureirin C can inhibit the activities of thrombin in vitro effectively.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number116384-24-8
-
Formula Weight272.3
-
Molecular FormulaC16H16O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (183.62 mM)
-
SMILESCOc1c(CCC(c(cc2)ccc2O)=O)ccc(O)c1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.A Systematic Review of the Botanical, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Profile of Dracaena cochinchinensis, a Plant Source of the Ethnomedicine "Dragon's Blood".Molecules, 2014, 19(7):10650-10669.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Methyl Laurate
Methyl laurate is a 12-carbon saturated fatty acid and an esterified version of lauric acid.
-
[Met5]-Enkephalin, a...
[Met5]-Enkephalin, amide is an agonist for δ opioid receptors as well as putative ζ (zeta) opioid receptors.Met-enkephalin circulates in several forms, some of which may be derived from proteins other than proenkephalin A, and plasma levels of both free native, and peptidase-derivable Met-enkephalin are modulated physiologically.
-
Geranyl acetate
Geranyl acetate is a monoterpene that has been found in C. sativa with diverse biological activities.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


